Have you been missing your monthly period lately but you’re not pregnant? You’re probably suffering from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a particular condition affecting a woman’s hormone levels. A woman with PCOS produces higher-than-normal amounts of male hormones. This hormonal imbalance results in missed menstrual periods and difficulty getting pregnant.
These are not the only signs and symptoms that you are likely to have PCOS. Read on, and you will learn more valuable information that will help you understand this illness further. Don’t wait for the signs to occur. It’s best that you know the symptoms, causes, treatments, and preventive measures to avoid PCOS from either happening or recurring.
What You Need to Know About Hormonal Disorder
PCOS is a problem woman experiences with her hormones that affect her during her childbearing ages (from 15 to 44 years old) According to Healthline, between 2.2 and 26.7% percent of women aged as mentioned suffer from PCOS. Regretfully, a lot of women have this illness, but they don’t know about it. In a study, up to 70% of women who have PCOS had not undergone a diagnosis.
PCOS impacts a woman’s ovaries, the reproductive organs producing progesterone and estrogen, the hormones regulating the menstrual cycle. The ovaries produce a small number of male hormones, also known as androgens. They release eggs for fertilization by a sperm which a male releases. The said release which takes place each month is also called ovulation.
It is essential to know that PCOS is a group of symptoms or a syndrome affecting a woman’s ovulation and ovaries. The illness’ main features include:
- High male hormones levels
- Skipped or irregular periods
- Cyst in the ovaries
What May Cause You to Experience PCOS Symptoms?
Doctors do not know exactly the causes of PCOS symptoms. However, they have the perception that high male hormonal levels stop the ovaries from making eggs and producing hormones in a normal manner. Among the common causes associated with excess production of androgen are insulin resistance, inflammation, and genes.
Insulin resistance
Up to 70% of women who have PCOS have insulin resistance. This means that their cells cannot properly use insulin. Insulin is a form of hormone the pancreas is producing to help the body properly use sugar.
Inflammation
A woman with PCOS frequently has higher inflammation levels in her body. Being overweight contributes as well, to inflammation. Some studies link excess inflammation to higher levels of androgen.
Genes
Studies have it that PCOS is hereditary too. This means that you are more likely to acquire PCOS if your mother or sister has it.
Common Symptoms of PCOS You Should Look Into
If you think you have a big chance of having PCOS due to the causes you just read, there are symptoms you should look into. Who knows, you might be feeling one, two, or all of these:
- Intermittent or irregular menstrual periods
Some women suffering from PCOS have less than eight menstrual periods each year.
- Heavy or excessive bleeding
There is a buildup of the uterine lining for a longer time. Therefore, the periods you get can sometimes be heavier than normal.
- Excessive hair growth
More than 70 % of women who have PCOS experience hair growth called hirsutism, on their face and body, particularly their belly, chest, and back.
- Acne
Male hormones tend to make the skin oilier than usual. They can also cause breakouts in some areas such as the face, upper back, and chest.
- Skin darkens
Possible formation of dark patches of skin in body creases like the ones in the groin, under the breasts, and on the neck.
- Headaches
Changes in hormones can trigger pains, particularly headaches, in some women.
- Male pattern baldness
There occurs the thinning and falling out of hair on the scalp.
- Weight gain
The majority of women suffering from PCOS are obese or overweight or obese.
How it affects your body

Having excess androgen levels can have a significant impact on your fertility, as well as your health’s other aspects. One of which is the effect on blood sugar levels. Other impacts are as follows:
1. Depression
Both the symptoms and hormonal changes like unwanted hair growth can unfavorably impact your emotions. A lot of women with PCOS result in experiencing anxiety and depression.
2. Sleep apnea
This sleep disorder causes repeated gaps or lapses in breathing at night, which certainly interrupt your sleep.
3. Infertility
If your ardent desire is to get pregnant, you should ovulate. Any woman who does not ovulate regularly does not release as many eggs for fertilization. PCOS is among the primary causes of infertility in women.
4. Metabolic syndrome
As earlier mentioned, the majority of women who have PCOS are obese or overweight. Relatively, both PCOS and obesity increase the risk for high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high LDL or bad cholesterol, and low HDL or good cholesterol. Altogether, these factors or effects are also known as metabolic syndrome, and they contribute to the high risk for illnesses such as stroke, heart failure, and diabetes.
5. Endometrial cancer
At the time of ovulation, there is the shedding of the uterine lining. Therefore, if you don’t ovulate regularly or monthly, the said lining tends to build up.
Know When You Need a Diagnosis
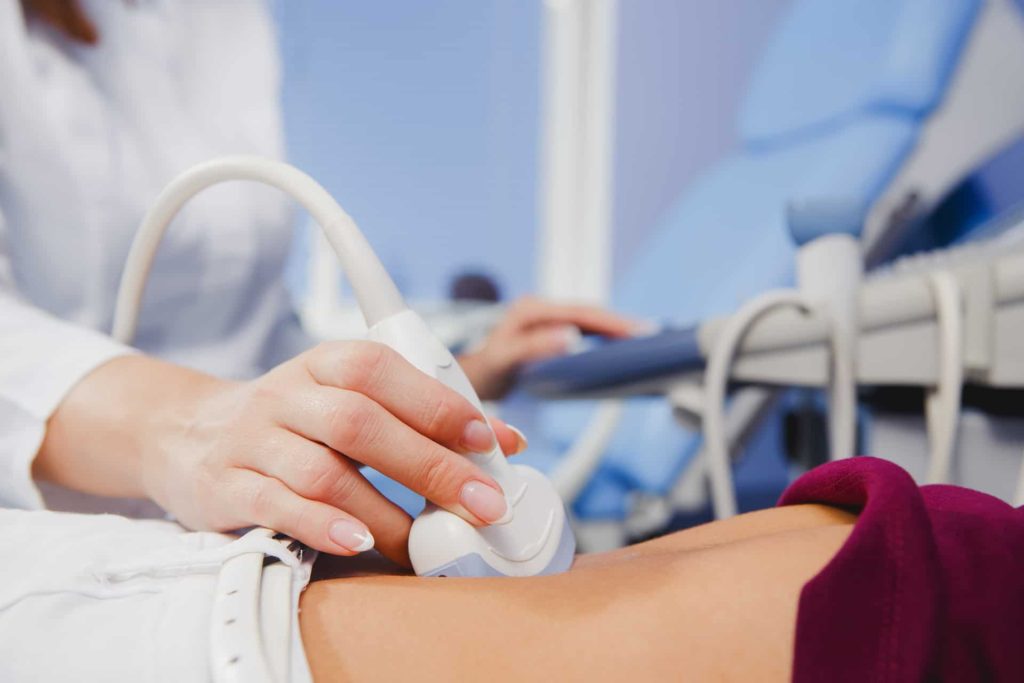
You’ll know when to undergo the PCOS diagnosis if you experience at least two of the three PCOS symptoms mentioned earlier. Also, the doctor should ask you if you have experienced the other symptoms like weight gain, body and face hair growth, and acne. Below are what you might go through for a diagnosis:
1. Pelvic exam
This procedure looks for certain problems or conditions with your ovaries or any other part of your reproductive tract. During the process, your doctor inserts gloved fingers in your vagina and thoroughly checks for any growth in your uterus or ovaries.
2. Ultrasound
This test is administered through the use of soundwaves which look into abnormal follicles, as well as other issues with the uterus and ovaries.
3. Blood tests
This series of tests checks for male hormones’ above-normal levels. Possibly, have blood tests to check your triglyceride, insulin, and cholesterol levels to assess your risk for related health conditions such as diabetes and heart failure.
Diet and lifestyle tips for treating PCOS

If you’ve been diagnosed with PCOS, don’t despair, and lose hope. There are ways to do to treat the illness. The treatment usually begins with changes in lifestyle such as diet, exercise, and weight loss. Losing between 5 and 10% of your total body weight can contribute to the regulation of your menstrual cycle, not to mention improve the symptoms of the said illness.
Weight loss helps improve cholesterol levels, reduce the risks for diabetes and heart disease, and lower insulin. More so, any diet that contributes to weight loss can contribute to the improvement of health conditions. Nevertheless, some diet types may have more benefits than others.
Several experts have it that half-an-hour of moderate to intense exercise, at least thrice a week can help a woman with PCOS lose weight. Losing weight through regular workout also enhances the insulin levels, as well as ovulation. Indeed, exercise is more beneficial if it is complemented with a healthy and balanced diet.
Now you have acquired more knowledge about PCOS — its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments. The next step to take is, based on the information you’ve discovered here, know your risk for the said illness. Are you likely to acquire it (for what possible cause) or, someone you know, perhaps, a loved one, is prone to having PCOS? Share this article and help the PCOS patients deal with their illness without all the worries and fears.
