Our brains are the seat of all we are. Every thought and action we perform is an output of our brain. So understandably the thought of an affliction striking the brain can be terrifying. Brain Tumor is a rare but devastating form of cancer accounting for 2% of all cancer cases worldwide.
Brain tumor refers to the abnormal growth and division of cells within the brain. Brain tumors can be either benign or cancerous and cancerous brain tumors are further split into primary brain tumors that start in the brain and secondary tumors that start elsewhere in the body and spread (metastasize) to the brain.
Whether benign or a malignant tumor can increase the volume of the brain which creates pressure in the tight skull space. The bony skull is extremely hard and rigid. Any encroachment in this tight space increases intracranial pressure which can lead to brain damage, coma, and even death.
Types Of Brain Tumours
The first major classification of types of brain tumors is benign and malignant tumors. Benign brain tumors are the least aggressive and slowest growing tumors. They do not have cancerous cells and have a good prognosis after treatment.
Malignant or cancerous brain tumors arise from brain cells, supportive cells, and other tissue found in and around the brain. These are high-grade tumors. Grading for tumors involves rating a growth on a scale of 1 to 4 with low-grade scores being 1 and 2, and 3 and 4 are high grade. Benign tumors are low grade which is slow growing, contained, less likely to spread, and unlikely to return after removal. On the other hand, malignant or cancerous tumors are high grade which means they are fast-growing, spread to surrounding tissues, and are more likely to return after removal.
Cancerous tumors are further divided into primary and secondary tumors.
Primary cancerous tumors originate within the brain itself while secondary tumors are a result of metastasis from tumors in other organ systems, commonly from the lungs.
Primary tumors are rarer and the most common types of primary brain tumors are gliomas and meningiomas. Gliomas affect the glial cells which are supportive cells in the brain that provide nourishment and structural support to neurons. Gliomas account for 50% of all primary brain tumors.
Symptoms Of Brain Tumors

The brain is a large and complicated organ. Symptoms of brain tumors depend on the size, type, and location of a tumor. Some common signs and symptoms are:
- Headaches, typically worse in the morning and progressively worsening over time.
- Persistent nausea
- Persistent vomiting
- Dizziness
- Progressive body weakness
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Behavioral or mood changes
- Vision problems
- Confusion and memory impairment
- Specific symptoms depend on the size of a tumor and its location. Based on this, some of the signs and symptoms that may be noticed are:
- Personality changes, less inhibition, poor judgment, etc. in frontal lobe tumors
- Language difficulties, poor memory, and hearing problems in temporal lobe tumors
- Sensory disturbances, progressive muscle weakness, etc. In parietal lobe tumors
- Visual disturbances or loss of vision in occipital lobe tumors.
- Loss of balance and coordination in cerebellar tumors.
- Changes in respiration, blood pressure, and heartbeat in brain stem tumors
This is a short summary of tumors in the major regions of the brain. As one goes more in-depth a variety of symptoms can be found ranging from loss of language comprehension to hallucinations.
Cause Of Brain Tumours
The underlying cause of brain cancer is not well known.
The two major factors implicated in the development of brain tumors is genetics and exposure to radiation. Gene mutations, sequence deletions, and loss of tumor suppressor genes are thought to contribute to the cause of brain tumors. A family history of tumors also increases the risk of developing the conditions. Certain genetic disorders such as neurofibromatosis, tuberous sclerosis, and Turner’s syndrome are associated with a higher risk of developing brain tumors.
Exposure to ionizing radiation has been linked to brain cancer especially in children. Exposure to Vinyl chloride, an industrial chemical used to manufacture PVC, has also been linked to brain cancer.
Other risk factors for brain cancer are:
- Age- risk increases with age, except for some forms of brain cancer that are more common in children
- Previous cancer diagnosis- a person who has had cancer elsewhere in the body is more at risk of developing brain cancer, especially childhood cancer and blood cancers such as leukemia and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- HIV/AIDS– people with HIV/AIDS are twice as likely to develop brain cancer than the general population.
Treatment Of Brain Tumours
The plan of treatment for brain cancer depends on the size, grade, and location of a tumor as well as overall patient health. Malignant brain tumors are usually surgically removed. However, surgical resection of an entire tumor may not always be feasible due to location or other factors like ease of access.
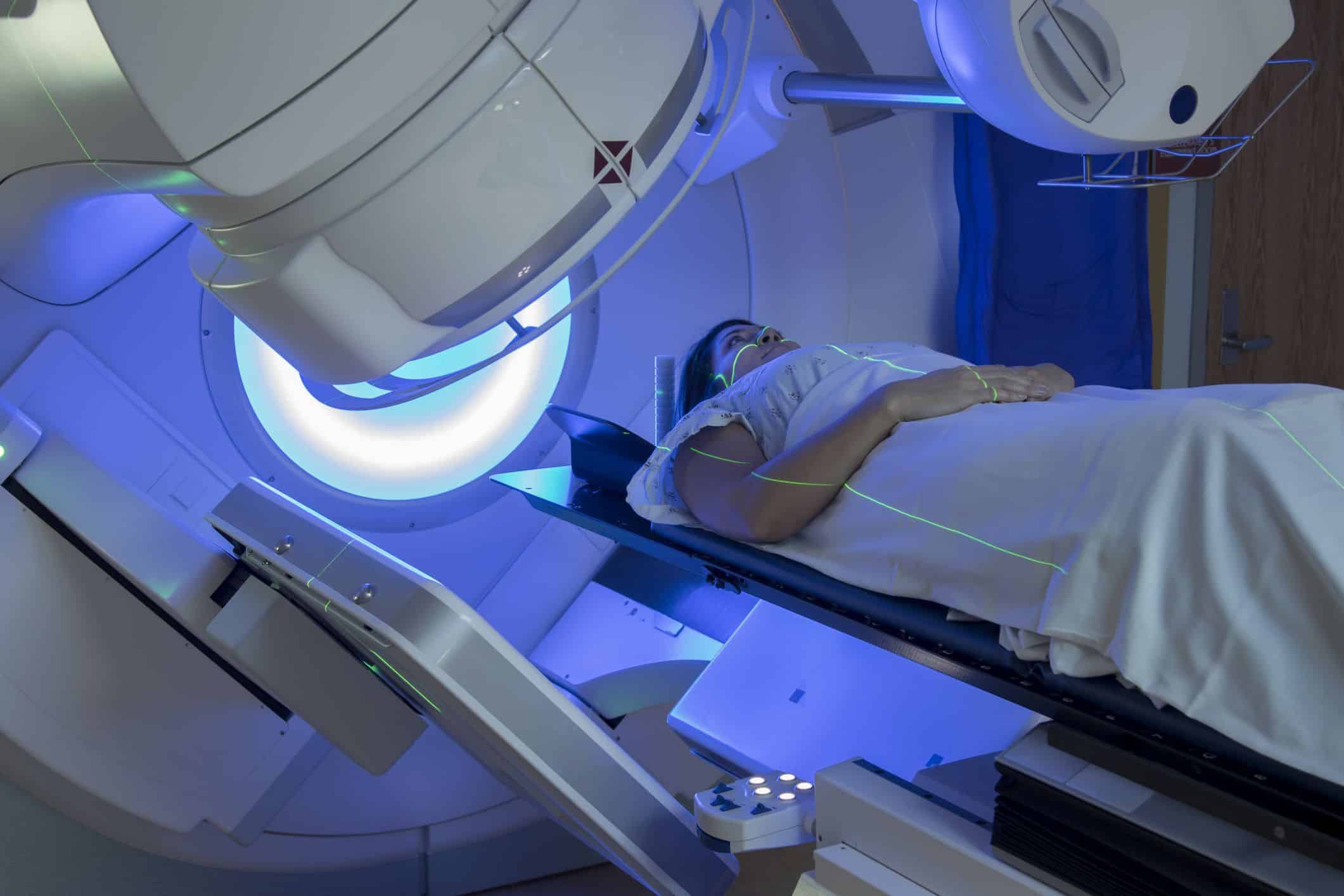
Radiation therapy is another treatment option that is commonly used to treat brain tumors. Radiation damages the DNA of cancer cells and stops their division and growth.
Chemotherapy or anti-cancer drugs are not always used since the blood-brain barrier prevents the transport of many of these drugs into the brain from the bloodstream.
A number of experimental therapies are also in development.
Early treatment of tumors can prevent further complications. 15% of people with brain cancer will survive for 5 years or more after diagnosis. Despite this, there is still hope. Prognosis depends on a lot of factors. Knowing your risk and following up on suspicious symptoms can help in early diagnosis. Stay alert to stay healthy.
